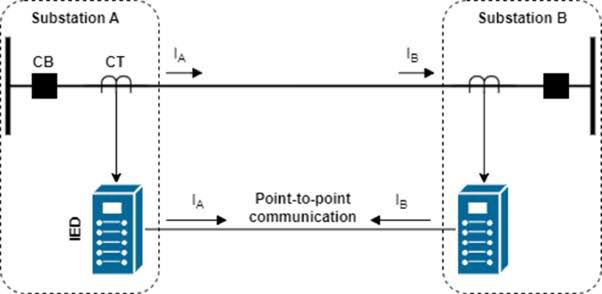
Current differential (87L) channel monitoring:
Once the communication channel(s) is supplied to the relay, the following has to be checked in the relay diagnostic menu:
---> The channel status should be continuously healthy. Interruptions in the channel indicate a problem with a channel and have to be investigated. Possible problems might include inadequate received signal level, loose connections, and communication noise. Communication noise is quantified by bit error ratio (BER) and can cause corruption of the 87L packet, potentially leading to 87L misoperation. Generally, a channel with BER less than 1 × 10-⁴ is considered appropriate for the 87L application.
--->An important indication of channel health is the lost packet count. Packets can be lost due to corruption because of the noise, channel switching, or channel fading; packets can also be lost if clocking of the communication system is not configured properly. If there is an increase, it indicates that channel is not healthy—this has to be further investigated and addressed.
---> Protection 87L function should be fully enabled.
--->Channel delay should be steady and within reasonable margin. Typically, a multiplexed channel can introduce 2 ms through 12 ms (sometimes even more) of the external round-trip delay compared to a dedicated fiber channel.
--->Channel asymmetry can be checked by injection of 1 per unit through current using GPS synchronized test sets and monitoring the differential current. A differential current close to zero indicates that there is no channel asymmetry on that particular channel. Maximum possible asymmetry has to be determined by creating worst-case communication path on the SONET/SDH ring and measuring differential current again. Channel asymmetry checks are not required in direct, single-fiber channel applications.
All channel-related problems have to be solved in coordination with the communications department.
At one terminal, a communication channel has to be interrupted by temporarily removing/replacing, for a short period of time, either the fiber connector or just the wire in case of galvanic interface. The relay records should be checked to indicate channel interruptions, possible lost or corrupted packets count, disabling and then enabling of the differential enabling, and disabling of the backup protection. The timing should be checked in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications. When a redundant channel is involved, timing to switch from main to backup communications path and vice versa should be checked. Some relays operate in a primary-hot standby mode while others operate in a primary-alternate mode. Appropriate tests have to be performed according to the design.
Verification of the relay ID is generally performed; relays applied over multiplexed channels are usually programmed to check whether the packets are received from the correct device. This eliminates misoperations when the channel is inadvertently looped back and the relay is measuring twice as much differential current as expected. By changing the ID temporarily to a “wrong” one, a check is performed to determine whether the relay’s 87L function is blocked.