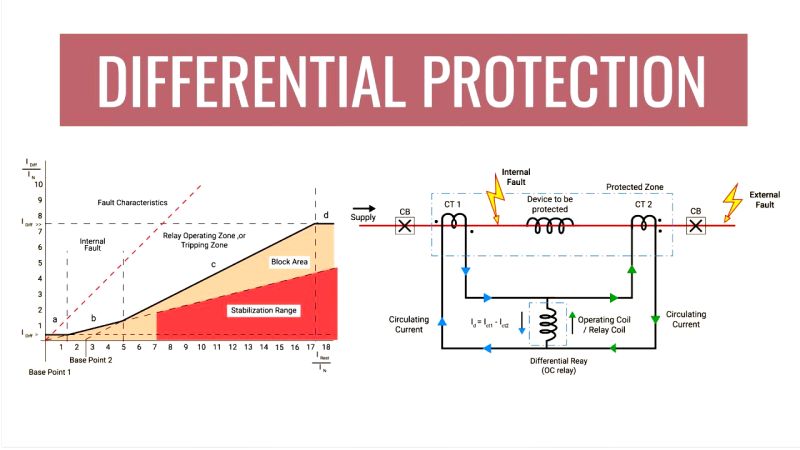
Differential relay protection is the principal means for protecting equipment such as transformers, generators, motors, and busbars. The protection scheme operates by continuously monitoring and comparing the currents entering and leaving a protected zone (the zone between the trip contacts). It will trip (i.e. actuate the circuit breaker) only if these two currents do not match due to an internal fault in the zone.
Working principle.
Current transformers (CTs) are installed at both ends of the protected equipment by the differential relay. In normal circumstances, the sum of the current entering the node and the current exiting the node should be equal. Any difference points to a fault in the protected zone:.
The relay compares the magnitude and phase of secondary currents received from both CTs.
The relay operates and sends a trip signal to the circuit breaker if the difference (differential current) exceeds an adequate value.
The tripping isolates the fault section and protects it further.
Diagram details.
CTs are placed at the input and output sides of the system.
The relay is connected to their secondary in parallel.
Under typical conditions, currents flow among CTs without energizing the relay.
The relay trips when internal faults disturb the balance.
Applications.
The purpose of transformer protection is to detect winding faults in the critical grid transformers and prevent them from a catastrophic failure.
Generator protection detects stator faults with great sensitivity, allowing errors to be quickly repaired and minimizing downtime in power plants.
The quick detection of faults in large industrial motors reduces repair costs.
Busbar protection quickly clears faults to limit disturbances at substations.
We can apply differential protection in both short and long zones over transmission lines by using pilot channels for communication between non-adjacent relays.
Advantages.
This device can detect very low amounts of current.
This trip breaker quickly limits damage to equipment and outage time.
Selectivity: Functions only for internal faults and does not trip from the outside.
They have a circuit breaker that doesn't trip vaguely.
Differential relays are designed to last long without requiring maintenance due to their simplicity and robustness.